Why should we use MPC signatures in the blockchain?
With Blockchain technology being implemented into a wide range of industries, safe private key management is now facing a big challenge. In contrast to Blockchain’s whole concept of ‘decentralization’, private keys are kept and stored by individuals. It’s led to many serious problems and risks such as loss, theft, destruction, etc. Therefore, to prevent such issues, it’s necessary to understand high-level encryption technologies for safe key management such as Multi-Signature (a.k.a. ‘Multisig’) and MPC.
MPC signature and Multisig may seem to operate on the same principles of technology, but by digging further, it is clear that the two have very distinct characteristics, with a different set of pros and cons. It is also notable that MPC signature has been receiving more attention than other encryption-based signing technologies, and thus leading to this blog post explaining how Penta MPC differs from Multisig.
What draws the line between MPC and Multisig is the formation of ‘private key’ which plays a critical role in signing.
For Multisig, when a complete private key is generated by each member, few signatures are gathered to create a multi-sign address. Then each member contributes their private key to sign their approval on the address and deliver the transaction.

Meanwhile, the entire scheme for approving a signature looks very different for MPC. MPC consists of members that hold a particle of a complete key and a full signature. When a request comes through the members gather the ‘derivative values’ of the private key to form what seems to be a ‘complete key’, thus creating a full signature. It is important to understand that no complete key is ever fully generated as every transaction operates on an ‘incomplete, particle key’.
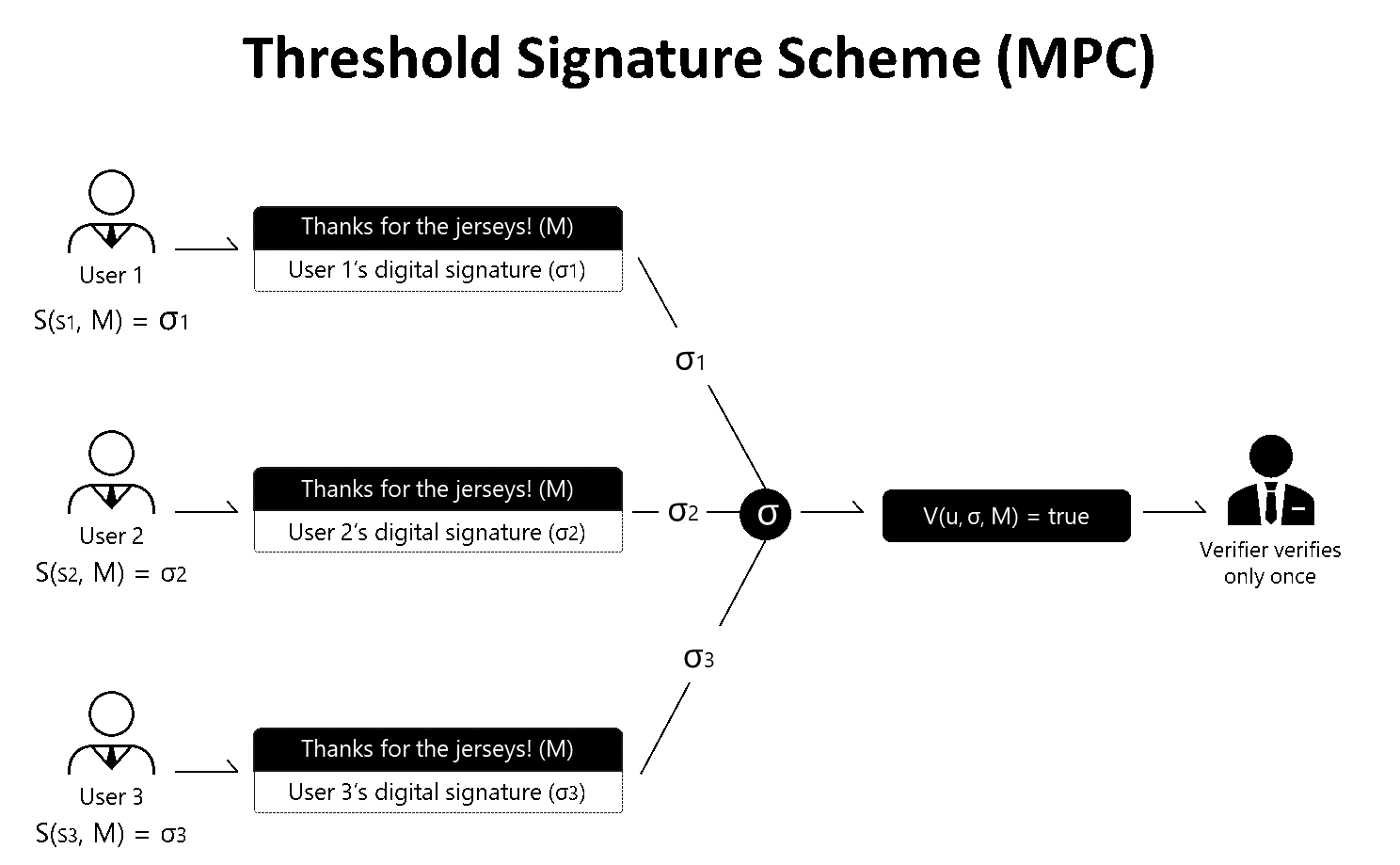
The environment that supports MPC and Multisig also varies. Multisig runs on UTXO blockchains and EOS, Ethereum smart contracts that support Multisig.
On the other hand, MPC signatures can be used on any public to private blockchains as long as it supports the elliptic curve signature algorithm. Luckily, most existing public and private blockchains that are up and running do support the necessary algorithms.
Differences also exist in the process of signing and verifying. When creating a signature for MPC, members take full control in approving or rejecting a transaction, thus, ensuring a fair distribution of responsibility and authority amongst the members. Moreover, because the data that is shared amongst the members gets swiped and renewed for every signing process, there is no risk in any secret values being stolen or exposed in any way.
However, Multisig does not ever reset the settings of its members, signing participants, nor private keys for approval, making all transactions work on a single loop of the same pattern. In other words, secret values necessary to approve the signatures never expire nor is reset/renewed, forming a very consistent pattern for calculations needed to approve a signature. This means that once the pattern is exposed to the hacker, every valuable data will be handed to its hand.
We can also take a look at the internal process for approving signatures and see how the signing workflow works distinctively for MPC and Multisig. The MPC does not need any additional procedures because the signature is completed when all the pieces of the signature are gathered during the signing process. However, Multisig must verify all n signatures because multiple signatures exist. Of course, as n increases, so does the verification time.
There is also a huge gap between the two technologies in how data is processed and recorded on the blockchain. With Multisig, all signing participants that have signed off the transaction is exposed with its address. This obviously makes it very convenient for anyone to go read all past history of transactions.
Meanwhile, MPC does not allow any identity nor sensitive data to be revealed. MPC only has one single public key for the entire group that is exposed to the blockchain. Therefore, no individual public keys are visible on any transactions recorded on the blockchain.
The two technologies performing with multiple party participation may fool some to think that they are identical. Though considering all aspects of safety, support environment, and scalability, MPC far outweighs Multisig in superiority. With MPC institutions, it is possible to manage all digital assets and securities safe and sound without having to risk valuable assets being stolen or lost. MPC will be the ultimate answer to creating a powerful, safe digital asset managing environments for all security experts in any field.